Table of Contents
Customer Journey คืออะไร? The customer's itinerary that businesses need to understand.
In a world of competitive businesses, understanding “Customer Journey” is becoming very important not only to attract new customers but also to build effective relationships with existing customers. Careful planning and management of this route can increase the chances of business success. Especially when using technology such as email marketing with CRM, a key tool to communicate with customers at every point of contact.
If your business wants to enhance its marketing strategy or develop CRM to meet the full range of Customer Journey requirements, CHIPHER, an expert in email marketing and CRM training, will help you create a differentiated customer experience. What? In this article, you will be able to understand every step of the way and apply these strategies to the best of your business.
What is a Customer Journey? Why is it important?
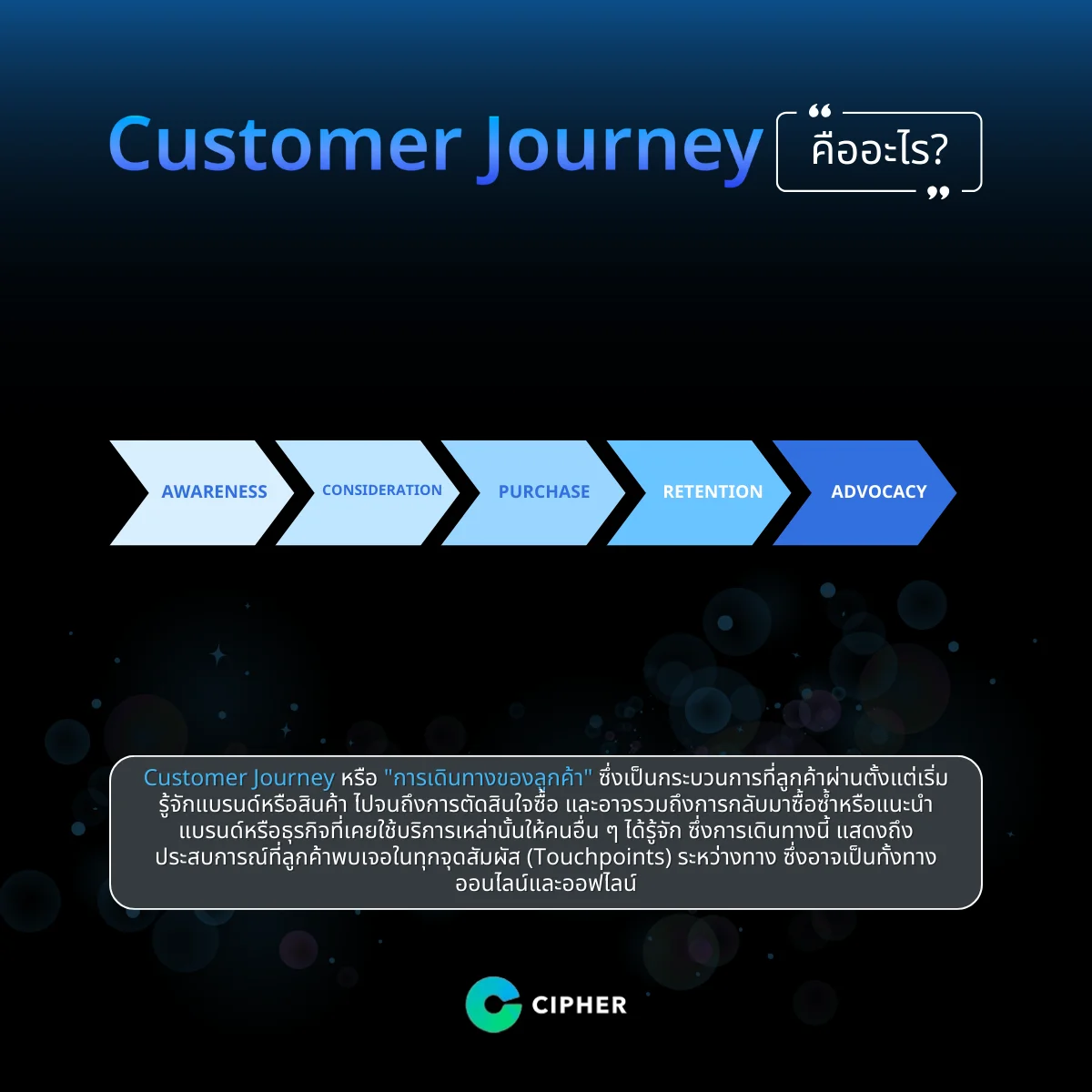
A Customer Journey refers to the process a customer goes through from the moment they first become aware of a brand or product, all the way to making a purchase decision. It may also include returning for repeat purchases or recommending the brand or service to others. This journey reflects the customer’s experience at every touchpoint along the way, whether online or offline.
This concept helps to visualize which media or organizations the target group must interact with in the business. When clearly seen, marketers can act as target groups and ask themselves how they feel. When meeting with each media outlet or using each service, they understand the target group’s perspective to develop their marketing strategies until they become customers. They have a high chance of returning to buy again and share it with their acquaintances.
Why do businesses need to focus on Customer Journey?
Customer Journey is important to today’s businesses because it allows a brand or business to understand customers at every stage of brand interaction, which directly affects sales success and customer satisfaction. Customer Journey’s route starts from Awareness, Consumption, Purchase, Retention, and the customer satisfaction. and Advocacy, each of which is important as follows:
- Awareness: Awareness: Customers are beginning to recognize brands, products, or services through various channels such as advertising, social media, relaying or searching for information themselves.
- Consideration: Afterwards, customers began to study and compare brands, products, or services to other options based on factors such as price, quality, reviews and user experience.
- Purchase: Customers later decide to purchase products or services through convenient channels such as e-commerce sites, online stores or platforms.
- Retention: Once a customer has purchased a product or used a service, then the brand must strive to satisfy their customers with good service, follow-up or offer special promotions to stimulate re-purchase.
- Advocacy (Sponsorship): Referred marketing. Customers who are satisfied may become brand supporters by introducing social media experience sharing or writing positive reviews.
Benefits of Understanding Customer Journey
Understanding that Customer Journey is What matters? This will give businesses a greater advantage than competitors due to the overall Journey or customer journey, allowing brands and businesses to offer different experiences depending on each customer as follows:
- Improve customer satisfaction: Customers often expect a smooth and comfortable experience at every stage. Understanding Customer Journey will help businesses improve their service delivery at each point, such as resolving complicated orders or delayed processes, creating a positive experience that affects customer satisfaction.
- Increase Sales and Conversion Rate: The Customer Journey analysis enables businesses to reduce sales loss opportunities, such as eliminating purchases in their baskets. When a business revises or determines a marketing strategy that matches customer behaviour and needs, it increases conversion rate and sales.
- Build brand loyalty: Customers will be loyal to a brand that meets their needs and provides a positive experience along the way. For example, follow-up after sales or offer promotions that suit customers’ taste the brand’s attention and make them buy or reuse services.
- Increase competitiveness in the market: In a time when customers have many choices, businesses that can create greater customer satisfaction will have an advantage over competitors.
- Build a positive brand image: Brand that values customer experience will be seen as caring and professional and will help build long-term customer confidence and lead to further communication.
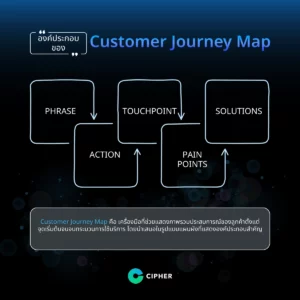
Key Elements of the Customer Journey Map
The Customer Journey Map is a tool that provides an overview of the customer experience from the start to the end of the service process. It is presented in the form of a diagram that shows five key components:
- Phase: It is a travel period or a process that customers must pass through to use products or services.
- Action: It is a behavior, action, or activity that the customer performs at each stage.
- Touchpoint: A point of contact or channel through which customers interact with the brand, whether they are media, employees or service channels.
- Pain Points: These are problems or obstacles that customers face at each stage or things that they don’t like that they need to be solved.
- Solutions: A solution to the problem, which is a solution to improve the customer experience.
The Customer Journey Map will help brands, businesses or organizations better understand their customers’ perspectives. This information will lead to product and service development and marketing strategies that best meet their needs.
Customer Experience Journey Analysis for Business Development
The Customer Experience Journey is an important process that helps businesses understand customer behaviour, needs and expectations at every stage of their journey, from brand recognition to post-purchase.
The Customer Experience Journey will enable businesses to improve their customer experience and increase opportunities for long-term satisfaction and good relationships between brands and customers. The key principles are as follows:
Important Touchpoints in Customer Journey
The Customer Experience Journey analysis needs to understand touchpoints, or points where customers interact with the brand, which are critical to their overall experience. The Customer Journey analysis of key touchpoints allows businesses to identify the steps that should be taken to improve their customer experience with touchpoints. Mainly:
- Prior to purchase: First touch points such as advertising and marketing campaigns, websites or social media, reviews and recommendations from other users.
- During purchase: Touchpoints are in the process of purchasing or channeling such as online or offline stores, payment procedures, and advice or additional information during decision making.
- Post-purchase: This is another important touch point that should not be overlooked after customers have purchased goods and services such as after-sales delivery or follow-up or review.
Identifying Pain Points and Gain Points
Pain Points and Gain Points are critical to customer satisfaction because identifying Pain Points and Gain Points enables businesses to set strategies that focus on problem solving and highlighting to impress and enhance customer loyalty.
- Pain Points are problems or obstacles that customers encounter during Customer Journey, such as complex payment procedures, slow response from customer service or incomplete product information.
- Gain Points are points where customers gain positive brand experience, such as fast service, special discounts, or effective support.
Therefore, identifying customer difficulties can be done by trying to understand your customer at the point that causes the difficulties they are facing. This can close the gap between the gap and the gap between the gap and the gap between the gap and the solution. Customers can easily change their Pain Points to Gain Points.
How to improve Customer Experience from Journey Map
Creating a Journey Map is a tool to help businesses see the overall picture of the Customer Journey and to effectively use information to improve their customer experience.
- In-depth analysis: Use data from analytical tools such as Google Analytics, CRM, or customer feedback to understand the behavior of each of the touchpoints.
- IMPROVEMENT OF IMPORTANT TOUCHPOINTS: Develop steps that create Pain Points, such as improving the payment system or answering support questions, to add Gain Points to offer special promotions or services that exceed expectations.
- Clear and continuous: Delivering messages that meet customer requirements at each stage, such as delivery status alerts or post-purchase recommendations.
- Strategy Testing and Improvement: Conduct a change test presented in the Journey Map and track results, and use customer feedback to improve strategies and improve customer experience for products and services.
Applying Customer Journey to Business
Customer Journey is an important tool that helps businesses to better understand and respond to customer needs. When applied to the business, it will help increase sales, strengthen relationships and create a positive customer experience.
Business Development Strategy with Customer Journey
- Key Touchpoints Improvements: Businesses should focus on touchpoints that affect customer decisions, such as improving UX/UI on the website or increasing convenient communication channels.
- Optimizing communication for each step: Use point-to-point messages such as sending additional product guidance emails after purchase or notification messages about special promotions.
- Improvement of after-sales experience: Systematic follow-up, such as submitting a satisfaction survey or offering discounts for next purchase
- The use of technology to support Customer Journey: Use AI or marketing tools to gather information and analyze customer behavior and use this information to predict or target the future.
Customer Journey's measure of success
The application of Customer Journey should be clearly measured for success using relevant indicators such as:
- Measure customer satisfaction with brand experience and the likelihood of customers introducing their business to others.
- Percentage of repeat customers after brand interaction
- Conversion Rate or rate of change from website visitor or interested person to customer who purchased the product.
- The collection of customer opinions in each touchpoint to analyze Pain Points and Gain Points.
Case Studies on the Success of Using Customer Journey
Spotify, a global music streaming leader, is committed to enhancing its music sharing features by collaborating with marketing companies to create a Customer Journey Map with the goal of:
- Analysis of user behavior from start-up to response to music shared by friends
- Use Empathy Map to understand the user’s feelings, thoughts, and actions on each touchpoints.
- Collect in-depth information through research and customer surveys
Spotify brings information from Journey Map to improve services by editing Pain Points to create a positive user experience, develop Omni Channel to connect mobile and social media, and design features that encourage easier and more fun music sharing. The results from this improvement have changed dramatically.
- User satisfaction is on the rise.
- The experience has become smoother.
- Brand loyalty has strengthened.
- Original User Becomes Brand Sponsor
This case study shows that understanding Customer Journey is what can lead to the development of products that truly meet the needs of users.
Techniques for Making Customer Journey Map Effective
Customer Journey Map is a tool to help businesses understand and analyze customer experiences at each stage, from brand awareness to post-purchase. Effective mapping requires insight, understanding customer behavior and clear planning. The techniques are as follows:
1. Detailed client data collection
Customer Journey Map is a customer’s journey, study of customer information and behaviour. This will help create a complete Journey Map, such as gender, age, product behavior, expectations and problems, as well as the way customers contact their brand. The methods of collecting information are as follows:
- Collect data from CRM systems: For example, HubSpot, a customer data collection tool, HubSpot can collect customer data on a single platform, either contact information or feedback from social media channels or reviews.
- Email Marketing: HubSpot can be marketed via email. Importantly, data from the CRM system can be used to analyze the results of various campaigns.
2. Specify Customer Touchpoints
Identifying touchpoints at each step helps to understand where customers interact with the brand. The main steps, starting from the first touch point, during the purchase and after the purchase, are to determine which touchpoints and actions are involved at each step to improve quality or measure results.
3. Use Persona to create a Journey Map
Persona is the modeling of characters or prototyping to represent customers. To target or target groups of customers, we will define details such as age, occupation, behavior, needs and problems for each individual, enabling better understanding of customers’ feelings or needs and leading to identifying Pain Points and Gain. Points to improve your brand and business
4. Analysis of Pain Points and Development Opportunities
Identifying issues can provide solutions and opportunities for businesses to improve their Customer Journey. The more customer information we have from our CRM or personalization, the more accurate solutions we can get.
5. Easy-to-understand Journey Map design
The easy-to-understand version of the map enables teams to use information effectively online. Tools such as HubSpot can be used to gather customer information from all channels and can be displayed as a dashboard to make it easier and easier for organizations to participate in improving, solving problems or developing your brand.
Summary
What is Customer Journey? Understanding its meaning, importance, and work steps will help you create a Customer Journey Map or a successful customer journey. Importantly, it can also be used to develop effective marketing strategies and increase the chances of your brand attracting and retaining customers, which is an important factor that will help your business grow in the future!
Frequently Asked Questions
Customer Journey plays an important role in helping businesses analyze good customer experiences, and we have collected common questions and answers for you!
What does “Customer Journey” mean?
Customer Journey refers to the process in which customers travel through all phases of business interaction, from the start of brand recognition to the end of their purchase of products and services. This process covers all customer touchpoints and behaviors, with the goal of providing the best customer experience.
What are the 5 stages of the Customer Journey?
Customer Journey can be divided into 5 important steps as follows:
- Awareness: It is the first step that customers recognize a brand or product through advertising, articles or peer advice.
- Consultation: Subsequent steps after knowing a brand or business, customers will have data to compare products, services or offers from different businesses and choose the best solution.
- Purchase (buy decision): the process by which a customer decides to purchase a product, service or subscription.
- Retention: Businesses are trying to keep existing customers back in service, such as through promotions, follow-up and after-sales services.
- Advocacy (recommendation):
Customers become brand sponsors by reviewing, recommending or sharing good experiences with others.
What does a Journey Map include?
A Journey Map is a visual representation of a customer’s journey process. The Journey Map data must be from a user’s point of view in order for the design team to further analyze and improve the product or service, which is divided into the following key components:
- User/customer: e.g., basic information such as age, occupation, needs and goals or expectations.
- Timeline/Phases: A sequence of customer steps, starting from before the service, during the service, and after the service.
- Touchpoints: is a channel where customers contact brands such as websites, applications, online stores or social media.
- Pain Points and Gain Points: Obstacles or problems encountered by customers such as incomplete information and delayed feedback.
- Actions (Actions): What the customer does at each stage and decisions
- Emotions (Emotions): such as satisfaction, dissatisfaction, or problems.
- Opportunities: e.g., improvement in ideas or solutions to improve customer satisfaction and improvements in touchpoints and experiences.